Sipoc For Software Development
Root cause analysis RCA is a class of problem solving methods aimed at identifying the root causes of problems or events. This template may be used for up to 6. Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification. Through our experiences we have assembled the Lean Six Sigma Toolkit which is one of the most complete and user friendly set of templates available. The toolkit assists Lean Six Sigma practitioners in keeping focused on their project work and not creating templates. The toolkit includes 3. Lean Six Sigma DMAIC methodology. For ease of use, the templates can be downloaded directly to your computer and are yours to keep and utilize in future projects. The templates have been developed in common formats such as MS Word, MS Excel or MS Power. Point. Included templates 5 Whys, Communication Plan, CTQ Chart, Dashboard Measurement Plan, Data Collection Plan, DMAIC Project Plan, DMAIC Tollgate Presentation, FMEA, Force Field Diagram, Implementation Plan Detailed, Implementation Plan High Level, Pilot Plan, Process Monitoring Plan, Process Value Analysis, Project Charter, Project Storyboard, Quick Win Identification, Response Plan, Sigma Calculator, SIPOC, Solutions Benefits and Implications, Solutions Prioritization Matrix, Solutions Selection Matrix, Stakeholder Identification, Stakeholder Management Plan, Stakeholder Map, Standardized Procedures, Team Meeting Agenda, Team Profile, VOC Research Plan, and XY Matrix. Six Sigma Green Belt Certification. A. A management methodology that uses only statistical tools to improve the customer experience. B. A customer focused problem solving methodology that uses powerful statistical tools to reduce variation and improve processes. C. A management methodology that is primarily focused on achieving financial results. Sipoc For Software Development' title='Sipoc For Software Development' /> D. A customer focused problem solving methodology used exclusively within the manufacturing sector. Which Role is not traditionally performed by a Green Belt
D. A customer focused problem solving methodology used exclusively within the manufacturing sector. Which Role is not traditionally performed by a Green Belt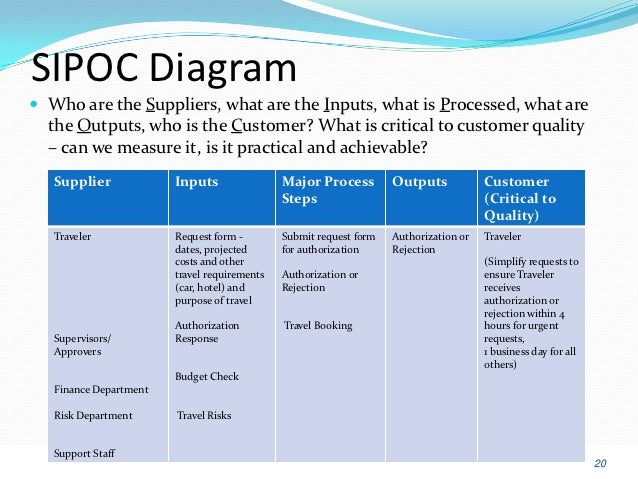 A. Data Gathering. B. Lead Small Projects. D. Coach and mentor other Six Sigma Practitioners. A. 2, 5, 1, 4, 3. B. 1, 2, 5, 4, 3. C. 3, 2, 1, 5, 1. D. 2, 1, 5, 4, 3. A. We can expect 3. B. It has a yield of 9. C. We can expect 3. D. It has a yield of 9. A. Bell shaped, a variance of 1, the meanmedianmode. Exemplo_seq.jpg/550px-Exemplo_seq.jpg' alt='Sipoc For Software Development' title='Sipoc For Software Development' />Value stream mapping software that you wont outgrow. Value stream mapping tools for value stream analysis and management not just drawing. Also Excel templates for. Smu assignments, smu mba assignments, smu mba summer solved assignments, smu mba summer assignments sem 1, smu mba sem 1 assignments, smu mba sem 1 solved assignments. B. Bell shaped, symmetrical about the mean, a single mode. C. Un Symmetrical about the mean, a natural tolerance of three standard deviations, unimodal. D. Symmetrical about the mean, bell shaped, discrete data. A shape referred to as Platykurtic is A. Flatter than the Normal Distribution. B. Narrower than a Normal Distribution. C. Same as a Normal Distribuiton. D. None of the above answers. A process is in control and stable. How-To-Guide/picture/Flow-chart--HR-management-process.png' alt='Sipoc For Software Development' title='Sipoc For Software Development' />Describe the type of variation that exists in the process. A. Special Cause variation. B. Natural Variation. C. Out the ordinary varation. D. Non random variation. A. 1,4,5. 10. Indicate which control chars is the most sensitive for measuring time as data. A. X bar R Chart. C. Individuals and Moving Range. Which one of the characteristics below does not reflect common cause variation A. Continue taking data measurements to confirm your belief. C. Stop and identify the Special Causes. D. Stop, identify the special Causes and eliminate them. A. The process is in control within the UCL and LCLB. The process appears to be too table and should be questioned. C. The process needs to be checked for special causes. Microsoft Toolkit 2 5 Beta 4 All Windows Os. D. The wrong control chart has been selected. The number of data points for a sample is 1. Indicate the approximate number of classes one needs to use for grouped dataIf the salary of professionals is inversely proportional to their age, it indicates relationship between the two variables A. No Correlation. D. Linear. 16. Select the corect mean, median and mode for the following sample 4,5,6,1,1,2,5,7,5. A. Process is capable. B. Process is capable but not centered. C. Process is highly capable and centered. D. Process is not capable. A process you are monitoring produces 1. What is the DPMO A. Using the same information from question 1. A. Consult with your legal department. B. Develop the appropriate control chart. C. It is still a normal distribution. D. Stop the process and bring it back into control. A. X Bar and R Chart. B. X Bar and the Standard Deviation Chart. C. X Bar and the Variance Chart. D. X Bar and the Mean Chart. An attribute chart can be represented by all of the following EXCEPT A. Select the key attributes of successful Six Sigma programs. Senior management commitment 2 High ROI projects 3 Projects with short durations 4 Proper funding 5 Well trained staff 6 Properly scoped projects. A. 1,2,4,5,6. 26. These provide support, resources and remove roadblocks. They have more in depth understanding of the methods measurements and interpretations of process measurements. They are referred to as A. Master Black Belts. C. Steering Committee. D. Process Owners. A. X bar R Control Chart. B. Pareto Chart. C. Cumulative Frequency Graph. What are the 3 key attributes of Six Sigma that best summarize why it is a compelling methodology for reducing variation and improving processes in the mind of Senior ManagementA. Data Driven, Creative, Streamlined. B. Customer Focused, Data Driven, ROI Oriented. C. Customer Focused, Statistical Emphasis, Conformity Driven. D. Data Driven, Methodical, ROI Oriented. A company using Six Sigma methodology is operating at a 9. What is its Sigma Level and failure rate A. Sigma, 3. 4 DPMOB. Sigma, 2. 33 DPMOC. Sigma, 2. 33 DPMOD. Sigma, 3. 4 DPMO3. A. Control Charts, Pareto Charts, Fish Bone Diagrams. B. Pareto Charts, Capability Indices, Control Charts. C. Pareto Charts, Fish Bone Diagrams, Scatter Plot Diagrams. D. Scatter Plot Diagrams, Pareto Charts, Correlation. A. Construct a histogram, Prepare Control Charts, Calculate Capability Indices. B. Construct a SIPOC, Prepare Control Charts, Calculate Cp and Cpk. C. Calculate the 3 measures of Central Tendency, Calculate Capability Indices, Prepare Control Charts. D. Prepare CTQs, Construct Control Charts, Calculate Capability Indices. The average time spent waiting in queue for a bank teller is 8 minutes. The Standard Deviation is 3. What is the tolerance of the process that exhibits the limits of normal variationA. B. 7 to 9 minutes. C. 6. 5 minutes to 9. D. 3 minutes to 1. The X Bar R Chart uses two control charts to monitor a process. What are they A. Mean and Standard Deviation. B. Mean and Range. C. Mean and Variance. D. Grand Average and Variance. Select the correct mean, median and mode for the following sample 5,3,3,6,3,4,1. A. 4. 8. 6,3,4. 35. What is the range and standard deviation for the above sample A. A process has the following X values 1,2,3,4,5 and Y values 2,4,6,8,1. What is the relationship between the two variables A. Positive and Linear. D. No Correlation. A. 5. 76,0. 00. 38. If the company is operating at 3 Sigma in the above example what is the percent conformance A. A process has a CP 1 nd a Cpk 1. Interpret these capability indices A. The process is centered but not capable. B. The process is not in control. C. The process is not capable. D. The Process is centered and capable. A. There is no difference between the terms both are used to indicate if a process is in control. B. Control Limits are set by the customers Specification Limits are derived by the process. C. Control Limits are derived by the process Specification Limits are set by the customer. D. Control Limits are typically 3 standard deviations from the mean Specification Limits are typically 3 standard deviations from the target. A process is out of control. Describe the type of variation that exists in the process. A. Random Variation. B. Special Cause Variation. C. Common Cause Variation. D. Inherent Variation. A. Take immediate action to identify root causes of the common cause variation. B. Increase the specification limits to ensure the process is capable. C. Continually and gradually improve the stable process. D. Stop the process, identify the causes, and eliminate them. You are monitoring a process and evidence of trending in the control chart. What is the most likely issue going onA. New operators. B. Different shifts. C. Changes in materials. D. Wear of machinery. Which item below most naturally follows the development of a SIPOC diagram A. A Process Map. B. Voice of the Customer. C. Critical to Quality Requirements. D. Project Charter. The Variance for an equipment installation is 3. What is the Standard Deviation A. Need to know the mean to compute. A. As one variable changes, one cannot predict a value for the other variable. B. As one variable increases, the other variable decreases. C. As one variable decreases, the other variable decreases. D. As one variable decreases, the other variable increases. The term Design of Experiments was coined by A. Crosby. 48. If the number of data points given is 1. HIstogram would be calculated as 4.
A. Data Gathering. B. Lead Small Projects. D. Coach and mentor other Six Sigma Practitioners. A. 2, 5, 1, 4, 3. B. 1, 2, 5, 4, 3. C. 3, 2, 1, 5, 1. D. 2, 1, 5, 4, 3. A. We can expect 3. B. It has a yield of 9. C. We can expect 3. D. It has a yield of 9. A. Bell shaped, a variance of 1, the meanmedianmode. Exemplo_seq.jpg/550px-Exemplo_seq.jpg' alt='Sipoc For Software Development' title='Sipoc For Software Development' />Value stream mapping software that you wont outgrow. Value stream mapping tools for value stream analysis and management not just drawing. Also Excel templates for. Smu assignments, smu mba assignments, smu mba summer solved assignments, smu mba summer assignments sem 1, smu mba sem 1 assignments, smu mba sem 1 solved assignments. B. Bell shaped, symmetrical about the mean, a single mode. C. Un Symmetrical about the mean, a natural tolerance of three standard deviations, unimodal. D. Symmetrical about the mean, bell shaped, discrete data. A shape referred to as Platykurtic is A. Flatter than the Normal Distribution. B. Narrower than a Normal Distribution. C. Same as a Normal Distribuiton. D. None of the above answers. A process is in control and stable. How-To-Guide/picture/Flow-chart--HR-management-process.png' alt='Sipoc For Software Development' title='Sipoc For Software Development' />Describe the type of variation that exists in the process. A. Special Cause variation. B. Natural Variation. C. Out the ordinary varation. D. Non random variation. A. 1,4,5. 10. Indicate which control chars is the most sensitive for measuring time as data. A. X bar R Chart. C. Individuals and Moving Range. Which one of the characteristics below does not reflect common cause variation A. Continue taking data measurements to confirm your belief. C. Stop and identify the Special Causes. D. Stop, identify the special Causes and eliminate them. A. The process is in control within the UCL and LCLB. The process appears to be too table and should be questioned. C. The process needs to be checked for special causes. Microsoft Toolkit 2 5 Beta 4 All Windows Os. D. The wrong control chart has been selected. The number of data points for a sample is 1. Indicate the approximate number of classes one needs to use for grouped dataIf the salary of professionals is inversely proportional to their age, it indicates relationship between the two variables A. No Correlation. D. Linear. 16. Select the corect mean, median and mode for the following sample 4,5,6,1,1,2,5,7,5. A. Process is capable. B. Process is capable but not centered. C. Process is highly capable and centered. D. Process is not capable. A process you are monitoring produces 1. What is the DPMO A. Using the same information from question 1. A. Consult with your legal department. B. Develop the appropriate control chart. C. It is still a normal distribution. D. Stop the process and bring it back into control. A. X Bar and R Chart. B. X Bar and the Standard Deviation Chart. C. X Bar and the Variance Chart. D. X Bar and the Mean Chart. An attribute chart can be represented by all of the following EXCEPT A. Select the key attributes of successful Six Sigma programs. Senior management commitment 2 High ROI projects 3 Projects with short durations 4 Proper funding 5 Well trained staff 6 Properly scoped projects. A. 1,2,4,5,6. 26. These provide support, resources and remove roadblocks. They have more in depth understanding of the methods measurements and interpretations of process measurements. They are referred to as A. Master Black Belts. C. Steering Committee. D. Process Owners. A. X bar R Control Chart. B. Pareto Chart. C. Cumulative Frequency Graph. What are the 3 key attributes of Six Sigma that best summarize why it is a compelling methodology for reducing variation and improving processes in the mind of Senior ManagementA. Data Driven, Creative, Streamlined. B. Customer Focused, Data Driven, ROI Oriented. C. Customer Focused, Statistical Emphasis, Conformity Driven. D. Data Driven, Methodical, ROI Oriented. A company using Six Sigma methodology is operating at a 9. What is its Sigma Level and failure rate A. Sigma, 3. 4 DPMOB. Sigma, 2. 33 DPMOC. Sigma, 2. 33 DPMOD. Sigma, 3. 4 DPMO3. A. Control Charts, Pareto Charts, Fish Bone Diagrams. B. Pareto Charts, Capability Indices, Control Charts. C. Pareto Charts, Fish Bone Diagrams, Scatter Plot Diagrams. D. Scatter Plot Diagrams, Pareto Charts, Correlation. A. Construct a histogram, Prepare Control Charts, Calculate Capability Indices. B. Construct a SIPOC, Prepare Control Charts, Calculate Cp and Cpk. C. Calculate the 3 measures of Central Tendency, Calculate Capability Indices, Prepare Control Charts. D. Prepare CTQs, Construct Control Charts, Calculate Capability Indices. The average time spent waiting in queue for a bank teller is 8 minutes. The Standard Deviation is 3. What is the tolerance of the process that exhibits the limits of normal variationA. B. 7 to 9 minutes. C. 6. 5 minutes to 9. D. 3 minutes to 1. The X Bar R Chart uses two control charts to monitor a process. What are they A. Mean and Standard Deviation. B. Mean and Range. C. Mean and Variance. D. Grand Average and Variance. Select the correct mean, median and mode for the following sample 5,3,3,6,3,4,1. A. 4. 8. 6,3,4. 35. What is the range and standard deviation for the above sample A. A process has the following X values 1,2,3,4,5 and Y values 2,4,6,8,1. What is the relationship between the two variables A. Positive and Linear. D. No Correlation. A. 5. 76,0. 00. 38. If the company is operating at 3 Sigma in the above example what is the percent conformance A. A process has a CP 1 nd a Cpk 1. Interpret these capability indices A. The process is centered but not capable. B. The process is not in control. C. The process is not capable. D. The Process is centered and capable. A. There is no difference between the terms both are used to indicate if a process is in control. B. Control Limits are set by the customers Specification Limits are derived by the process. C. Control Limits are derived by the process Specification Limits are set by the customer. D. Control Limits are typically 3 standard deviations from the mean Specification Limits are typically 3 standard deviations from the target. A process is out of control. Describe the type of variation that exists in the process. A. Random Variation. B. Special Cause Variation. C. Common Cause Variation. D. Inherent Variation. A. Take immediate action to identify root causes of the common cause variation. B. Increase the specification limits to ensure the process is capable. C. Continually and gradually improve the stable process. D. Stop the process, identify the causes, and eliminate them. You are monitoring a process and evidence of trending in the control chart. What is the most likely issue going onA. New operators. B. Different shifts. C. Changes in materials. D. Wear of machinery. Which item below most naturally follows the development of a SIPOC diagram A. A Process Map. B. Voice of the Customer. C. Critical to Quality Requirements. D. Project Charter. The Variance for an equipment installation is 3. What is the Standard Deviation A. Need to know the mean to compute. A. As one variable changes, one cannot predict a value for the other variable. B. As one variable increases, the other variable decreases. C. As one variable decreases, the other variable decreases. D. As one variable decreases, the other variable increases. The term Design of Experiments was coined by A. Crosby. 48. If the number of data points given is 1. HIstogram would be calculated as 4.